- anatomy
- Cardiovascular
- clearptconcepts
- dpt
- dptstudent
- fsbpt
- medicalstudents
- neuro
- neuroanatomy
- neurophysiotherapy
- NPTE
- NPTEP
- NPTEPrep
- npteprepcourse
- physicaltherapist
- physicaltherapistassistant
- physicaltherapy
- PhysicalTherapyFuture
- physicaltherapystudent
- physiotherapist
- physiotherapiststudent
- physiotherapy
- physiotherapystudents
- pt
- pta
- ptstudent
- StudyGroup
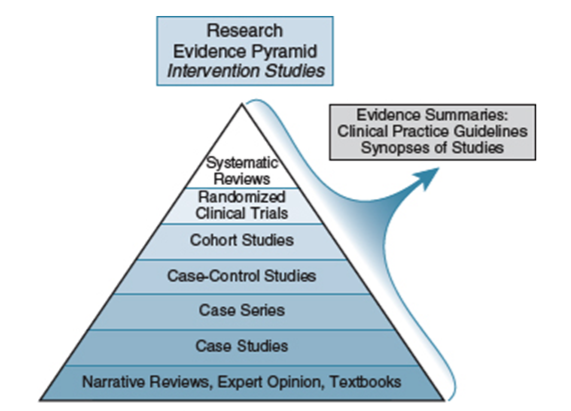
The tibiofemoral joint possesses two degrees of freedom: flexion and extension in the sagittal plane and, provided the knee is at least slightly flexed, internal and external rotation.
Internal and external (axial) rotation of the right knee.
A, Tibial-on-femoral (knee) rotation. In this case the direction of the knee rotation (internal or external) is the same as the motion of the tibia; the femur is stationary.
B, Femoral-on-tibial rotation. In this case the tibia is stationary and the femur is rotating. The direction of the knee rotation (external or internal) is the opposite of the motion of the moving femur: external rotation of the knee occurs by internal rotation of the femur; internal rotation of the knee occurs by external rotation of the femur.
Ref: Kinesiology Of Musculoskeletal System
Keep your basics strong .Keep Revising .Happy Studying .
Reach out to us to get more details at clearptconcepts@gmail.com
You can also enroll at www.clearptconcepts.com